Last Updated on February 14, 2023 by Admin
Explain the concept of segmentation and provide an example of how it is used in a SOC.

Expert Answer and Explanation
Segmentation refers to dividing an extensive network into smaller sub-networks, known as segments, to improve network security and performance. This is accomplished by establishing logical or physical boundaries within a network, which separate various network components and regulate the information flow between them.
Segmentation aims to increase security, boost performance, and streamline administration (Petryschuk, 2019). Security Operations Centers (SOCs) frequently employ segmentation to safeguard the internal network and shield sensitive data from online dangers. By dividing the internal network into distinct security zones, each with its own set of security policies and controls, a SOC can segment its network.
For instance, a SOC might have a segment of its internal network dedicated to sensitive data like financial and personal information. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures are used to protect this section to make sure that only authorized users can access the data. To keep hackers from accessing sensitive data, the internal network segment is also isolated from the rest of the network.
Additionally, segmentation of the network based on various business functions illustrates segmentation in a SOC. For instance, systems used by the finance department might be found in one segment, while those by the human resources department in another. This way, if an attacker breaches the financial data segment, they will not be able to access the human resources department or general data. This lowers the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks by enabling each segment to have security policies and controls.
In conclusion, segmentation is a critical aspect of a SOC’s security strategy and is used to divide the network into smaller, more secure sub-networks. This helps to prevent breaches, limit the damage caused by attacks, and improve overall network performance.
References
Petryschuk, S. (2019, April 9). Network Segmentation: What It Is & How It Works. Retrieved from Auvik Networks Inc.: https://www.auvik.com/franklyit/blog/network-segmentation/
Topic 2 DQ 2: Provide two examples of breach detection products and describe the use of each in a SOC using a real-world example.
Expert Answer and Explanation
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems are typical examples of breach detection products. These tools can be used in a SOC to find and address security flaws. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) SIEM systems are made to gather and examine log data from various servers, firewalls, and application sources.
This log data is used to recognize security threats and take appropriate action (Gillis & Rosencrance, 2022) . For instance, if a SIEM system notices an unusual pattern of logins coming from a particular IP address, it may notify a SOC analyst. This behavior might indicate that a hacker is trying to access the system without authorization. A healthcare organization used a SIEM system in the real world to find a system breach.
The SIEM system was set up to gather log information from various sources and examine it for indicators of an attack. The system alerted the SOC analyst when it discovered an unusual pattern of logins coming from a particular IP address. Sensitive patient data was not lost due to the breach because the analyst could react quickly and mitigate it.
Intrusion detection systems (IDS)
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are designed to find unauthorized access points to networks and other systems. IDS can be installed in a network to watch for indications of an attack in incoming and outgoing traffic (Lutkevich, 2021) . For instance, a network-based IDS could notify a SOC analyst if a lot of data is being transferred from a system quickly.
Such actions signal that a hacker is trying to steal sensitive information from the system. A financial institution used a network-based IDS in the real world to find a system breach. If there was excessive data being transferred from the system, the IDS was set up to notify the SOC. When the alert was raised, the SOC analyst found that a hacker had infiltrated one of the systems and was stealing private customer information. Sensitive customer data was not lost due to the breach because the analyst could react quickly and mitigate it.
References
Gillis, A. S., & Rosencrance, L. (2022, December 09). security information and event management (SIEM). Retrieved from Security: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/security-information-and-event-management-SIEM
Lutkevich, B. (2021, October 7). What is an intrusion detection system (IDS)? Definition from SearchSecurity. Retrieved from Security: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/intrusion-detection-system
Assignment 1: Benchmark – SOC Tools and Technologies
The purpose of this assignment is to identify the tools and technologies needed for a successful SOC.
Highly trained employees and structured processes allow the SOC to understand threats more clearly. The combination of people, processes, software, and hardware allows a SOC to fully discover and understand where an attack may come from and what techniques are being used to try to penetrate the company networks and infrastructure. It is imperative that the appropriate tools be selected for the SOC and that the security professional possess the ability and skills to manage these SOC systems.
Students will have a sound understanding of the technologies and methods utilized to defend systems and networks. They will be able to describe, evaluate, and operate a defensive network architecture, employing multiple layers of protection using technologies appropriate to meet mission security goals.
Select five hardware and five software tools and technologies you would recommend for the SOC you proposed and designed in Topic 1 assignments. Create a chart that summarizes the following information about each hardware and software selection by completing the worksheet “SOC Tools and Technologies.” This will be the SOC Tools and Technologies section in the IT Proposal.
- Provide the specific name of each hardware/software tool/technology.
- Explain specifically what the hardware/software does.
- Justify each hardware/software selection by validating that the systems chosen will provide an appropriate security architecture.
APA style is not required, but solid academic writing is expected.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Refer to the LopesWrite Technical Support articles for assistance.
This benchmark assignment assesses the following programmatic competencies:
B.S. Cybersecurity
3.1: Develop appropriate security architecture by demonstrating a solid understanding of information system platforms
5.4: Explore system security monitoring tools and techniques, e.g., incident response, event monitoring, data recovery, system management administration (M7, M9, O2)

Assignment: Benchmark – Security Driven Solutions
The purpose of this assignment is to conduct a security gap analysis.
A security gap analysis is used to find vulnerabilities in an information system and uncover areas that need security controls implemented. This process serves as an opportunity for IT to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
Using the same corporation you selected from the “Company Profiles” in the Topic 1 assignment, develop a security survey, perform a gap analysis, and explain how you will evaluate and mitigate internal threats. Create a gap analysis chart and address the following:
- Develop a security survey for the company and identify at least 10 information systems resources and their vulnerabilities.
- List the possible threats to the information systems resources.
- Use the security survey information to perform a gap analysis. Use a scale of 1–5 to identify the risk to each information resource. Keep in mind they cannot all be fives.
- Explain how you will mitigate each identified risk. If you are implementing a security control, document the security control and explain its purpose.
- Explain how the SOC will evaluate and mitigate internal threats. Include discussion about how internal threats are a component of the security gap analysis.
- Describe the laws that provide U.S. entities the authority and other motivations that may prompt an organization to perform cyber operations.
- List the phases of a well-organized cyber operation and describe the goals and objectives of each phase.
- Identify alternate cyber environments (SCADA, real time systems, critical infrastructures).
APA style is not required, but solid academic writing is expected.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are not required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite.
This benchmark assignment assesses the following programmatic competencies:
B.S. Cybersecurity
2.1: Explain how crypto can be used, strengths and weaknesses, modes, and issues that have to be addressed in an implementation (e.g. key management), etc. (M7, M9, O2, O13)
Use Coupon Code: NEW30 to Get 30% OFF Your First Order
Other Solved Questions:
SOLVED! An 83-year-old resident of a skilled nursing
SOLVED!! Describe the clinical manifestations present in
SOLVED! Robert Haines was discharged from the hospital
SOLVED! Identify your specialty area of NP practice
SOLVED!! Post an explanation of at least two opportunities
SOLVED!! Select a patient that you examined during the last
FAQs
What is a network segment
A network segment is a portion of a computer network that is separated from other portions of the network by a physical or logical boundary. The purpose of network segmentation is to help improve the security, performance, and manageability of the network.
A network segment can be defined by a variety of factors, such as physical topology, geographic location, or functional role. For example, a network segment may be composed of all the devices and connections that are physically located in a particular building or department, or it may be a logical segment defined by a VLAN or subnet.
By segmenting a network, organizations can limit the impact of security breaches, reduce network congestion, and simplify network management. For example, a network segment may be designed to separate guest Wi-Fi traffic from internal employee traffic, or to isolate sensitive financial data from the rest of the network.
Overall, network segmentation is a critical practice for improving the security and performance of computer networks, and the use of network segments is a common way to implement network segmentation.
Network segmentation examples
Network segmentation refers to the practice of dividing a computer network into smaller, more secure subnetworks. Here are some examples of network segmentation:
- Guest and employee networks: A common practice in corporate environments is to have a separate network for guests and visitors that is segregated from the internal employee network.
- Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance: In order to meet PCI compliance requirements, organizations are required to segment their network to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive credit card data.
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices: IoT devices, such as smart thermostats or security cameras, can pose a security risk if they are connected to the same network as computers and servers. Segregating IoT devices onto a separate network can help prevent attacks.
- Remote access: Organizations can segment their network to provide secure remote access for employees, contractors, or partners.
- Departmental networks: In larger organizations, it can be beneficial to segment the network based on department or business unit, which can help limit the impact of security breaches or other network issues.
Network segmentation diagram
Here is a simple network segmentation diagram:
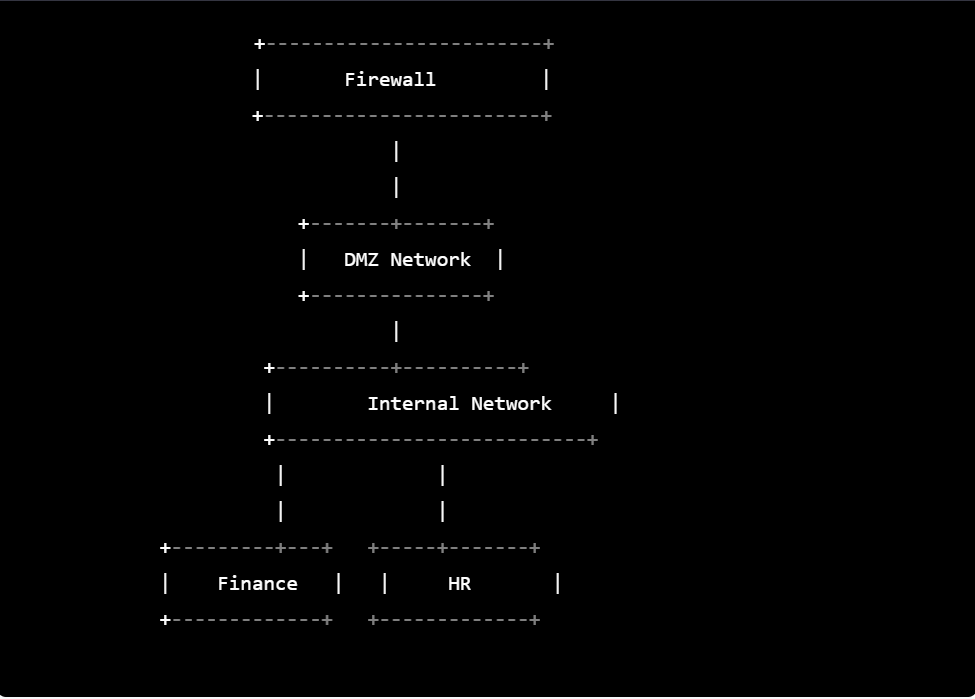
In the above diagram, the network is segmented into three parts:
- DMZ Network: This network is typically used to host public-facing servers, such as web servers or email servers. It is separated from the internal network by a firewall to limit the exposure of the internal network to the public internet.
- Internal Network: This is the main network that connects all the internal resources, such as computers, servers, and printers. It is protected from external threats by the firewall.
- Departmental Networks: The Finance and HR departments have their own subnets and are separated from each other for security reasons.
Overall, network segmentation helps to reduce the attack surface and mitigate the risk of a security breach by limiting the lateral movement of threats within the network.
Types of network segmentation
There are several types of network segmentation that can be used to help improve the security and performance of a computer network. Here are some common types of network segmentation:
- VLAN Segmentation: VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) allow a physical network to be logically segmented into multiple virtual networks. This can be used to separate traffic based on function, department, or user group.
- Subnet Segmentation: Subnetting allows a large network to be divided into smaller, more manageable subnetworks. This can be useful for limiting the spread of network traffic or isolating segments for security purposes.
- DMZ Segmentation: A Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is a separate network segment that sits between an organization’s internal network and the public internet. It is used to provide a buffer zone to help protect internal resources from external threats.
- Host-Based Segmentation: Host-based segmentation involves using software-defined firewalls or other security tools to segment individual hosts or devices within a network. This can be useful for implementing granular security policies and limiting lateral movement of threats within a network.
- Application Segmentation: Application segmentation involves segmenting a network based on specific applications or services. This can be useful for improving performance or limiting the impact of a security breach.
Overall, network segmentation is a critical practice for improving the security and performance of computer networks, and the choice of segmentation type depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization.
Network segmentation vs Vlan
Network segmentation and VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) are related concepts that are often used together to help improve the security and performance of computer networks. However, they are not exactly the same thing.
Network segmentation is the practice of dividing a computer network into smaller, more secure subnetworks. The purpose of network segmentation is to limit the impact of security breaches, reduce network congestion, and simplify network management. Network segmentation can be implemented in a variety of ways, such as using physical or logical boundaries, and can be based on factors such as geography, function, or security requirements.
VLAN, on the other hand, is a technology that allows a physical network to be logically segmented into multiple virtual networks. VLANs enable multiple networks to coexist on a single physical network, and devices on different VLANs can communicate with each other as if they were on separate physical networks. VLANs are often used to separate traffic based on function, department, or user group, and can be used to implement network segmentation.
So, while VLAN is a specific technology for implementing network segmentation, network segmentation is a broader concept that can be implemented in a variety of ways, including the use of VLANs. VLAN is just one of many tools that can be used to implement network segmentation, and it is often used in conjunction with other segmentation techniques, such as subnetting or DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) segmentation.
Network segregation vs segmentation
Network segregation and network segmentation are related concepts, but they have different meanings.
Network segregation is the practice of separating different networks from each other to reduce the risk of security breaches. Network segregation can be implemented using physical or logical boundaries, such as firewalls or VLANs, and is often used to isolate sensitive or critical systems from less secure parts of the network. The goal of network segregation is to limit the ability of attackers to move laterally within a network and reduce the potential impact of a security breach.
Network segmentation, on the other hand, is the practice of dividing a single network into smaller subnetworks, often based on function or security requirements. The goal of network segmentation is to improve the security, performance, and manageability of a network by limiting the scope of potential security breaches, reducing network congestion, and simplifying network management. Network segmentation can be implemented using techniques such as VLANs, subnets, or DMZs.
In summary, network segregation and network segmentation are both important practices for improving the security of computer networks, but they refer to different things. Network segregation is the practice of separating different networks from each other, while network segmentation is the practice of dividing a single network into smaller subnetworks.

